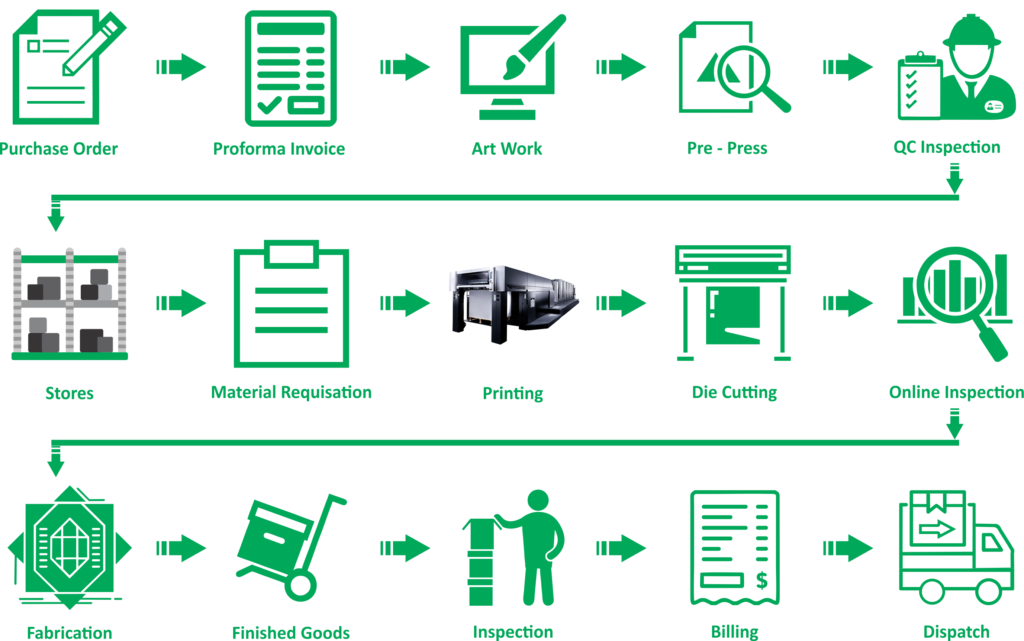
Here are some key aspects of pharmaceutical packaging:
- Protection and Preservation:
- Physical Protection: Packaging shields pharmaceutical products from physical damage, such as impact, compression, and vibration during transportation and handling.
- Barrier Properties: Packaging materials are selected to provide a barrier against moisture, light, oxygen, and contaminants, preserving the stability and effectiveness of the medication.
- Safety and Tamper Resistance:
- Tamper-Evident Features: Packaging often includes features to indicate whether the product has been tampered with, ensuring the safety of the end-user.
- Child-Resistant Packaging: Certain medications, especially those intended for household use, may be packaged in child-resistant containers to prevent accidental ingestion.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Serialization and Traceability: Packaging may include serialization and traceability features to comply with regulatory requirements. This helps in tracking and authenticating products throughout the supply chain.
- Labeling: Detailed and compliant labeling is crucial for providing essential information to healthcare professionals and consumers, including dosage instructions, warnings, and expiration dates.
- Dosage Forms and Administration:
- Unit Dose Packaging: Some medications are packaged in unit dose forms for convenient and accurate dosing.
- Pre-Filled Syringes and Vials: Injectable medications often come in pre-filled syringes or vials, ensuring accurate dosage and reducing the risk of contamination.
- Innovative Packaging Solutions:
- Smart Packaging: Emerging technologies enable the development of smart packaging solutions, such as temperature-sensitive indicators or electronic monitoring devices to track the condition of the product.
- Compliance Packaging: Packaging designs that promote medication adherence, including blister packs with days of the week or time of day labeling.
- Environmentally Friendly Packaging:
- Sustainable Materials: Some pharmaceutical companies are increasingly adopting sustainable and eco-friendly packaging materials to reduce their environmental impact.
- Patient-Centric Packaging:
- Ease of Use: Packaging is designed with the end-user in mind, aiming for easy opening, clear instructions, and user-friendly features.
- Accessibility: Packaging may consider the needs of patients with physical limitations, ensuring accessibility for a diverse range of users.
Pharmaceutical packaging is a highly regulated field due to the critical nature of the products involved. It involves collaboration between pharmaceutical manufacturers, packaging suppliers, and regulatory bodies to ensure compliance with safety and quality standards.


















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.